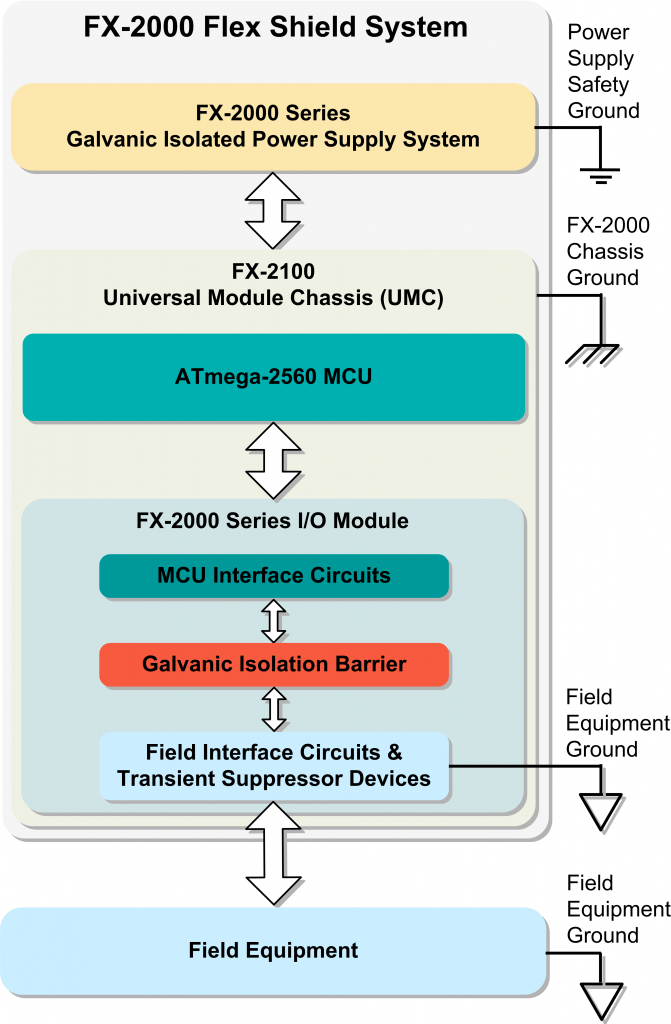
How Galvanic Isolation Works
Galvanic isolation is a design technique that separates electrical circuits to eliminate harmful stray voltages. Signals can pass between galvanically isolated circuits, but unwanted stray voltages, such as those produced by AC or DC power transients or differences in ground potential are effectively blocked. All FX-2000 series I/O modules, communications modules, and power power supplies are galvanically isolated.
Voltage Transient Protection
Voltage transient and ground offset protection are critical to system performance and reliability. Electrical fast transient (EFT) voltage events produced by switching inductive loads such as motors, solenoids, and relays; electrostatic discharge (ESD) caused by the buildup of potential on people or equipment; or voltages developed by ground offsets can damage or corrupt MCU logic circuits producing unpredictable operating behavior that is difficult to diagnose and resolve.
To prevent this, FX-2000 series I/O modules employ a galvanic isolation barrier using a combination of transformer based RF digital isolators and transient protection devices to block destructive EFT, ESD, and unwanted ground-differential-voltages from appearing in the sensitive MCU electrical environment.
Serial Data Ground Offset Protection
When communicating with field equipment over RS-232, 422 or 485 serial-data links, a difference in potential between separate chassis grounds can generate unwanted ground-offset-potential that can degrade serial-data-communications and, in some cases, damage the data transceiver. The FX-2000 serial-data-transceiver modules are specifically designed to meet this challenge using galvanic isolation and integrated EFT/ESD protection to ensure reliable data signaling in hostile electrical environments.